- [ Polynon ]
- [ About ]
A tool for mapping cognition and a philosophical investigation
It opens up possibilities for understanding how consciousness sculpts the contours of perceived reality and how the hidden potentials of noumena may influence the observer’s experience.
[ What is the polynon ]
A polynon is a conceptual geometric entity, a polytope of which vertices are non-events and its edges, holograms.
Through an analytic idealist lens, the polynon proposes a holographic framework where the observer and reality unfold as interconnected projections. It aims to reveal the intricate architecture of cognition by disentangling the relationships between sensory experiences (phenomena), internal representations (phantasiai), and the ineffable underlying realities (noumena).
The term Polynon combines the Greek root poly- meaning “many” or “much,” with the suffix -non, which draws from the concept of non-events—occurrences outside conventional temporality, causality, or sensory interaction. It also echoes the philosophical notion of noumena in Kantian thought: “things-in-themselves” that exist beyond perception.
-
1
Geometric Cognition
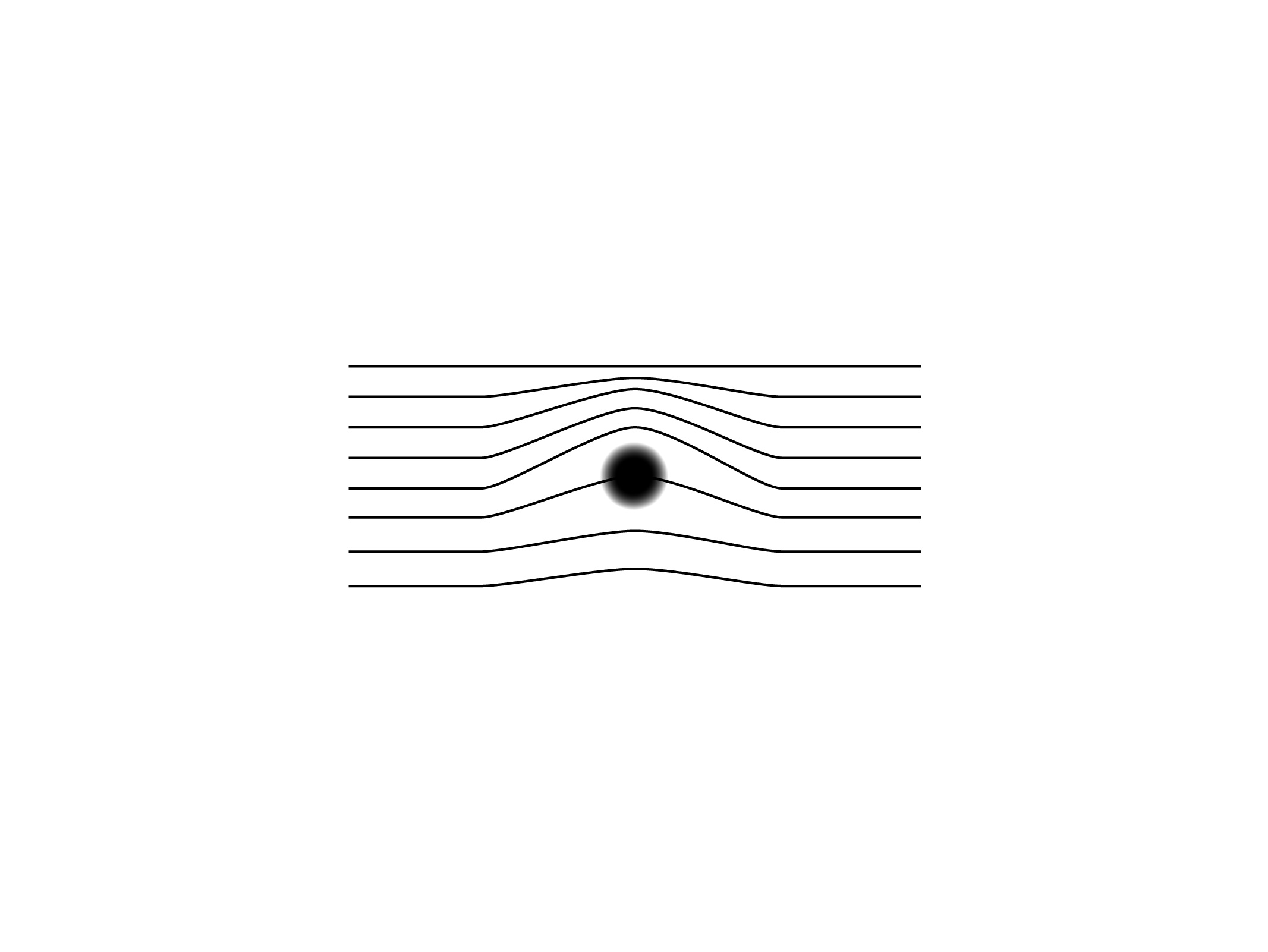
Consciousness is modeled through geometric and topological structures that underlie perception, forming a framework for how experience is spatially organized.
-
2
Cognitive Gravity
A principle that defines how meaning, memory, and attention are shaped by gravitational-like dynamics within cognitive space, stabilizing perception around attractors.
-
3
Phenomena, Phantasia, Noumena
A layered model of interaction between sensory experience (phenomena), internal representation (phantasia), and the unseen structures of reality (noumena).
-
4
Observer and Wavefunction Superposition
The observer is treated as a functional mechanism within consciousness, existing in superposition with physical reality and shaping what becomes measurable or knowable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Polynon?
The polynon is a geometric framework for understanding consciousness, perception, and cognition. It models how experience unfolds through structured dimensions shaped by attention, memory, and meaning.
Is the polynon a scientific theory or a philosophical system?
The polynon bridges both domains. It draws from cognitive science, geometry, and systems theory while offering a foundational ontology for modeling subjective experience.
What does "Cognitive Gravity" mean in this context?
Cognitive Gravity refers to the forces that shape perception, meaning, and truth. It models how attention stabilizes around conceptual attractors, forming coherent experiences and memory structures.
How is the polynon different from traditional models of mind?
Traditional models often treat mind as a computational or emergent phenomenon. The polynon treats cognition as geometrically structured, with consciousness as primary and perception as a spatial unfolding.
What role does the observer play in the polynon?
The observer is not external but embedded. The polynon treats the observer as a self-reflective function within consciousness, a mechanism through which perception organizes and reflects reality.
Can the polynon be applied to technology or AI?
Yes. Polynon informs the design of cognitive systems, visualizations, and interpretative architectures by modeling how meaning forms and evolves, guiding more intuitive and context-aware tools.
Does the polynon align with any existing philosophical traditions?
It resonates with aspects of idealism, process philosophy, and phenomenology, while introducing novel geometrical and topological mechanisms for understanding mind and meaning.
Is the polynon a finished model or an evolving system?
The polynon is evolving. As a living framework, it adapts through dialogue, experimentation, and integration, constantly refining how it maps consciousness and cognition across domains.
