- [ Polynon ]
- [ Whitepaper ]
Cognitive Gravity: A Polynonial Architecture for Experience
- [ Abstract ]
Gravity, the most immediate condition of embodiment, resists integration with quantum theory, pointing to a deeper epistemological fracture. This dissonance is used here as argument for a cognitive interpretation of reality, where gravity is a structuring principle of perception. In this framework, geometric cognition plays a central role, with the mind arranging information spatially through embedded and embodied topologies. Thus, cognitive gravity is proposed to model how experience is organized, and how memory, language, and truth are shaped by gravitational dynamics that stabilize within a manifold of perception and consciousness.
- [ Keywords ]
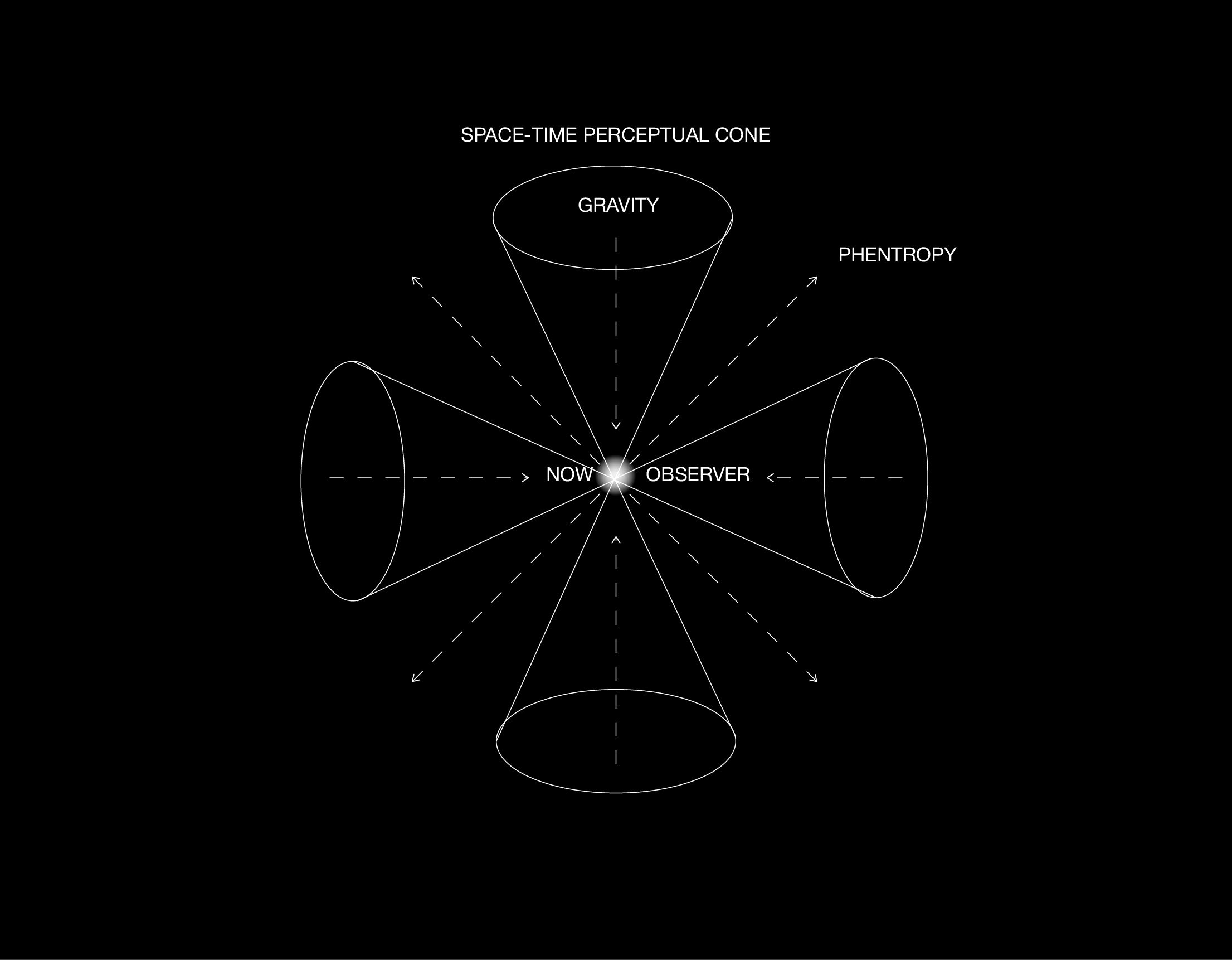
Cognitive Gravity, Consciousness, Observer, Noumena, Perception, Cognitive Relativity, Reality Construction, Phentropy, Manifold
- [ Cite ]
- [ Roibu, T. (2025) Cognitive Gravity: A Polynonial Architecture for Experience. ]
1 Introduction
2 Cognitive Gravity
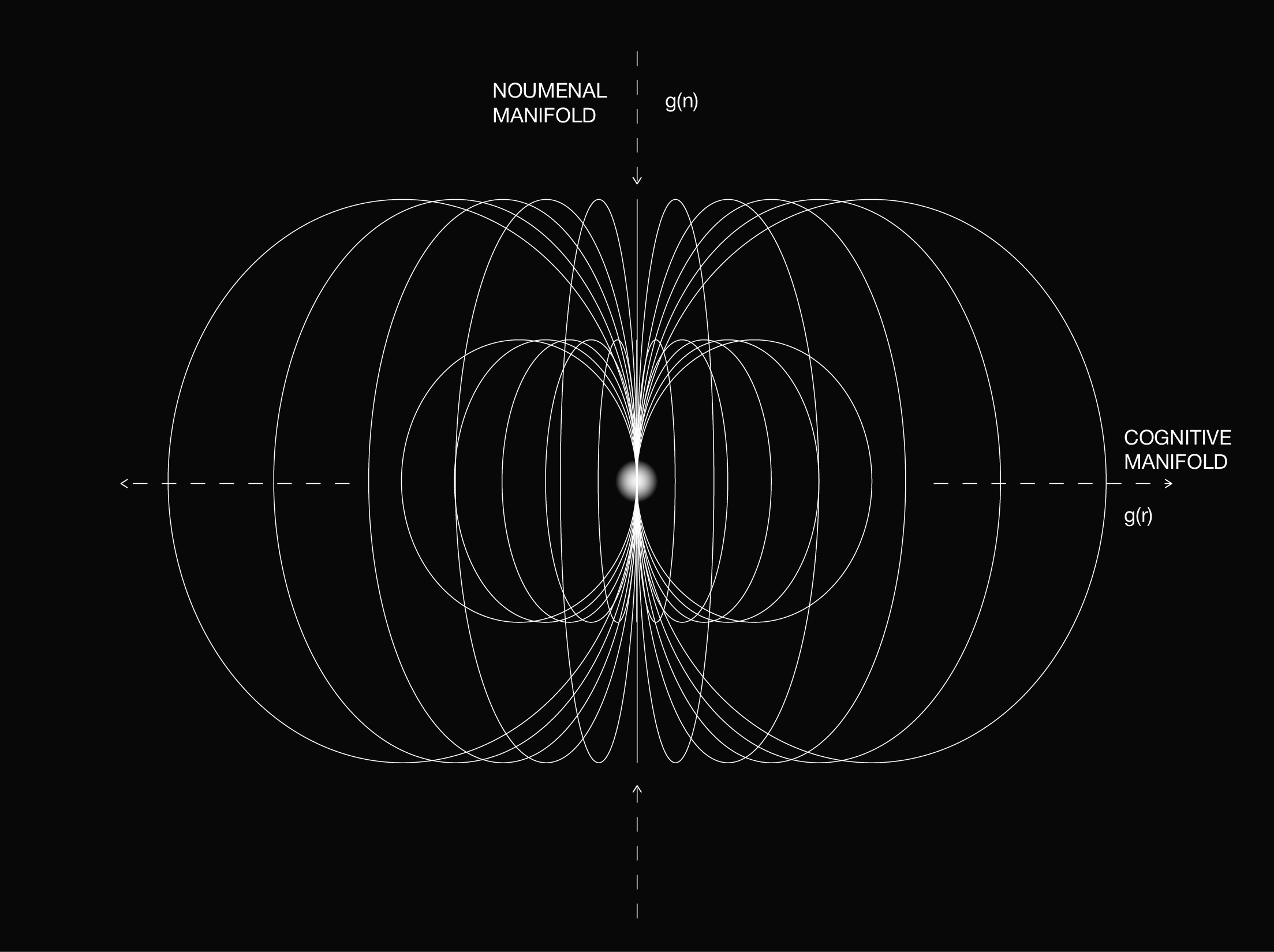
2.1 The noumenal gradient
2.2 The cognitive gradient
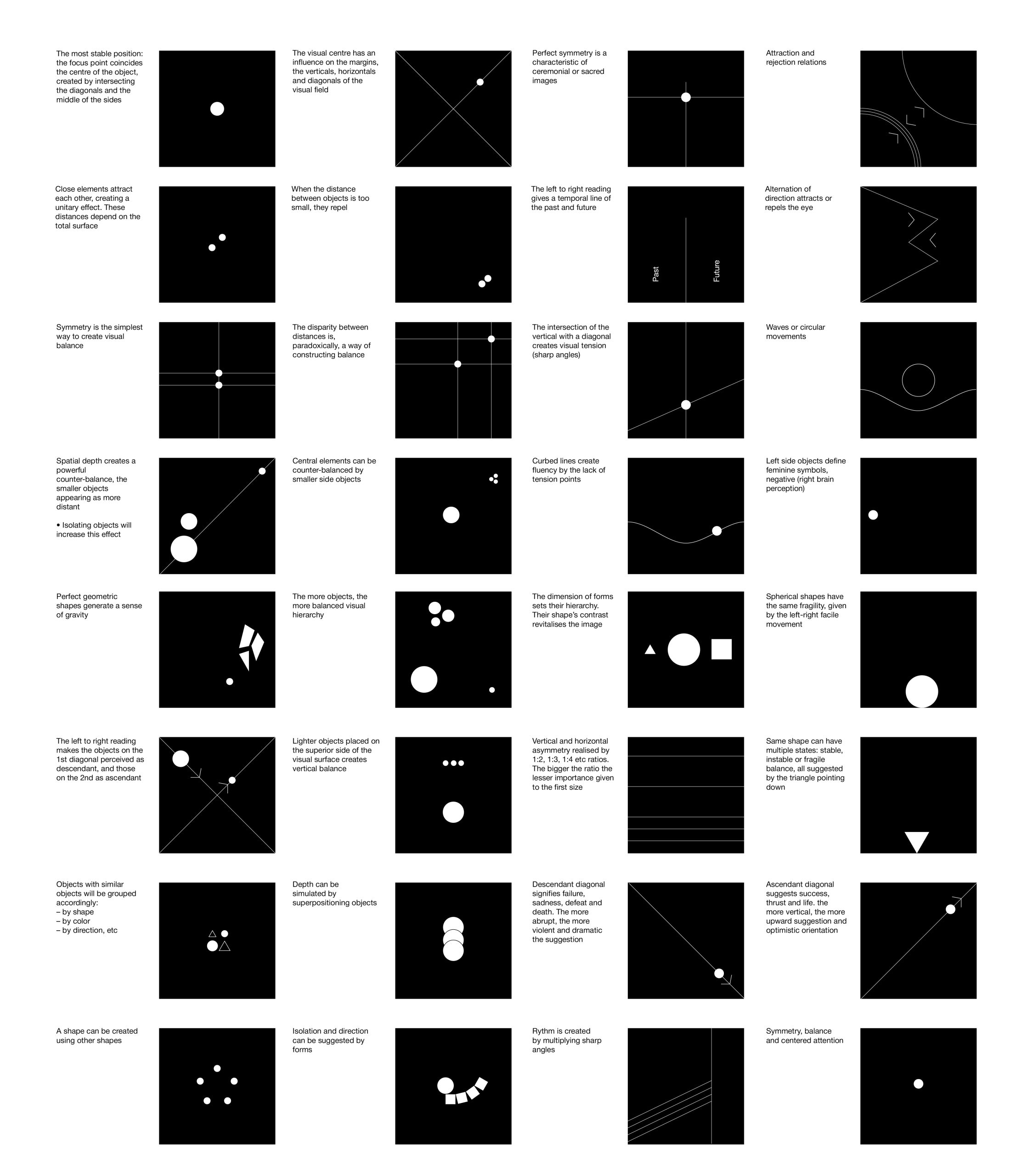
3 Geometric Cognition
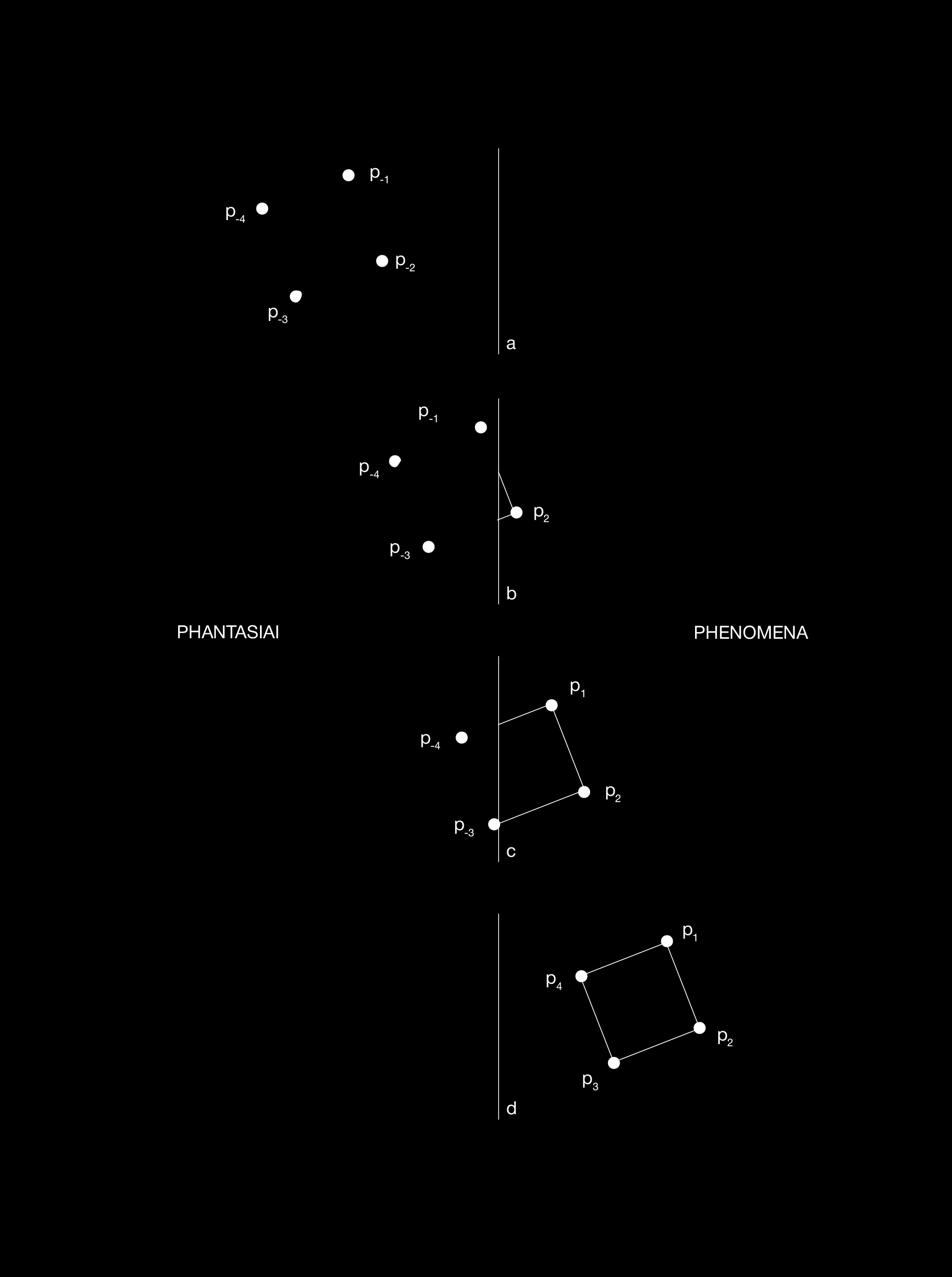
3.1 Phantasiai et Phenomena
the visual effect being the results of the competiton between the mechanism of showing the mental image and the mechanism involved in focal attention, becoming a competition between seeing “real” images and imagining them. (Knauer, Maloney, 1913).
3.2 Attention
3.3 Perceptual pleasure
In other words, it is the visual interpretation of patterns that leads to the feeling of pleasure.
Under all these circumstances, information becomes its own reward, whether it is useful or not. (Ming Hsu, 2019)
3.4 Beauty
3.5 Truth
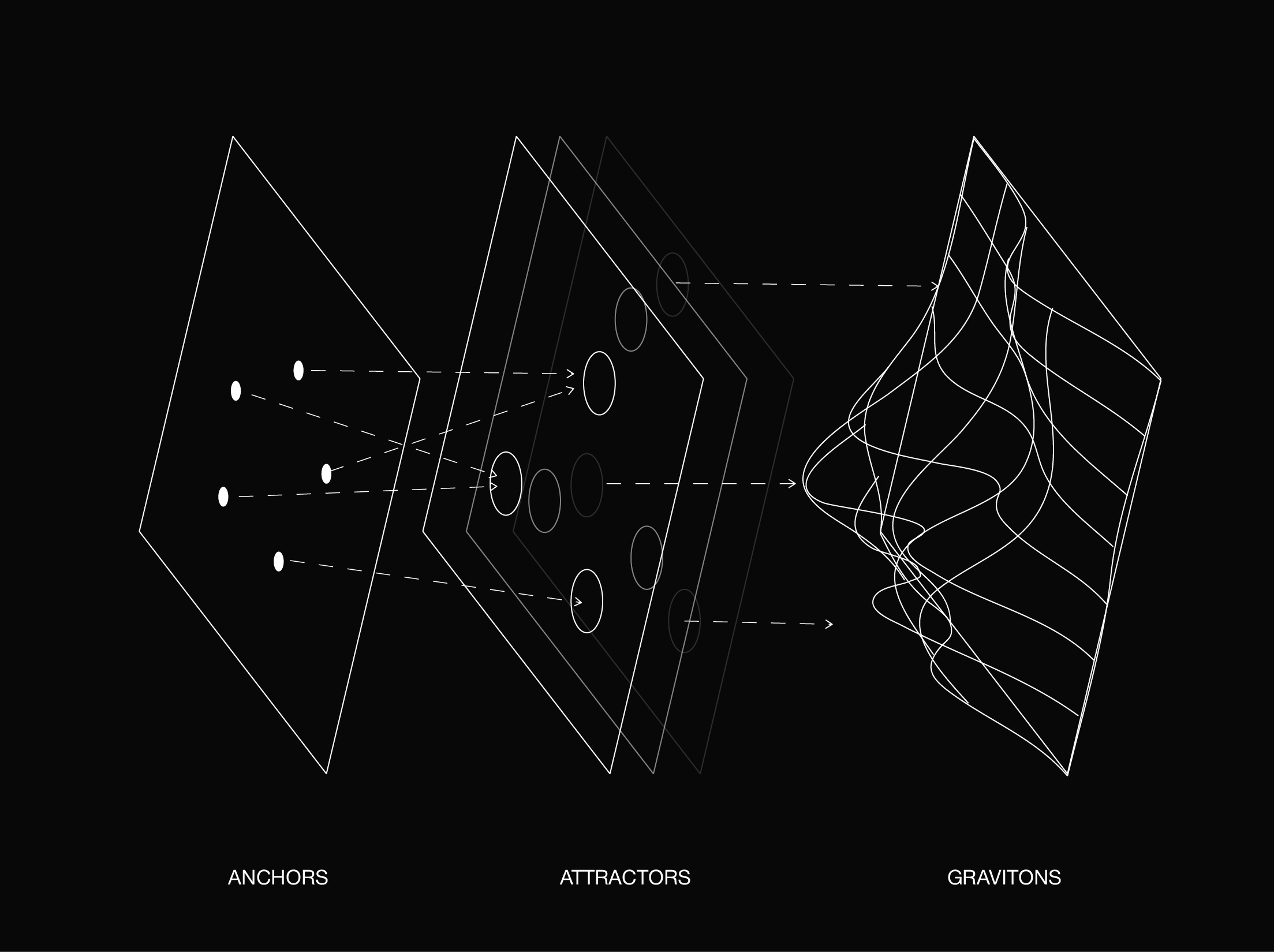
4 The Grammar of Cognitive Gravity
5 The Gravity of Lived Events
Love is metaphysical gravity.
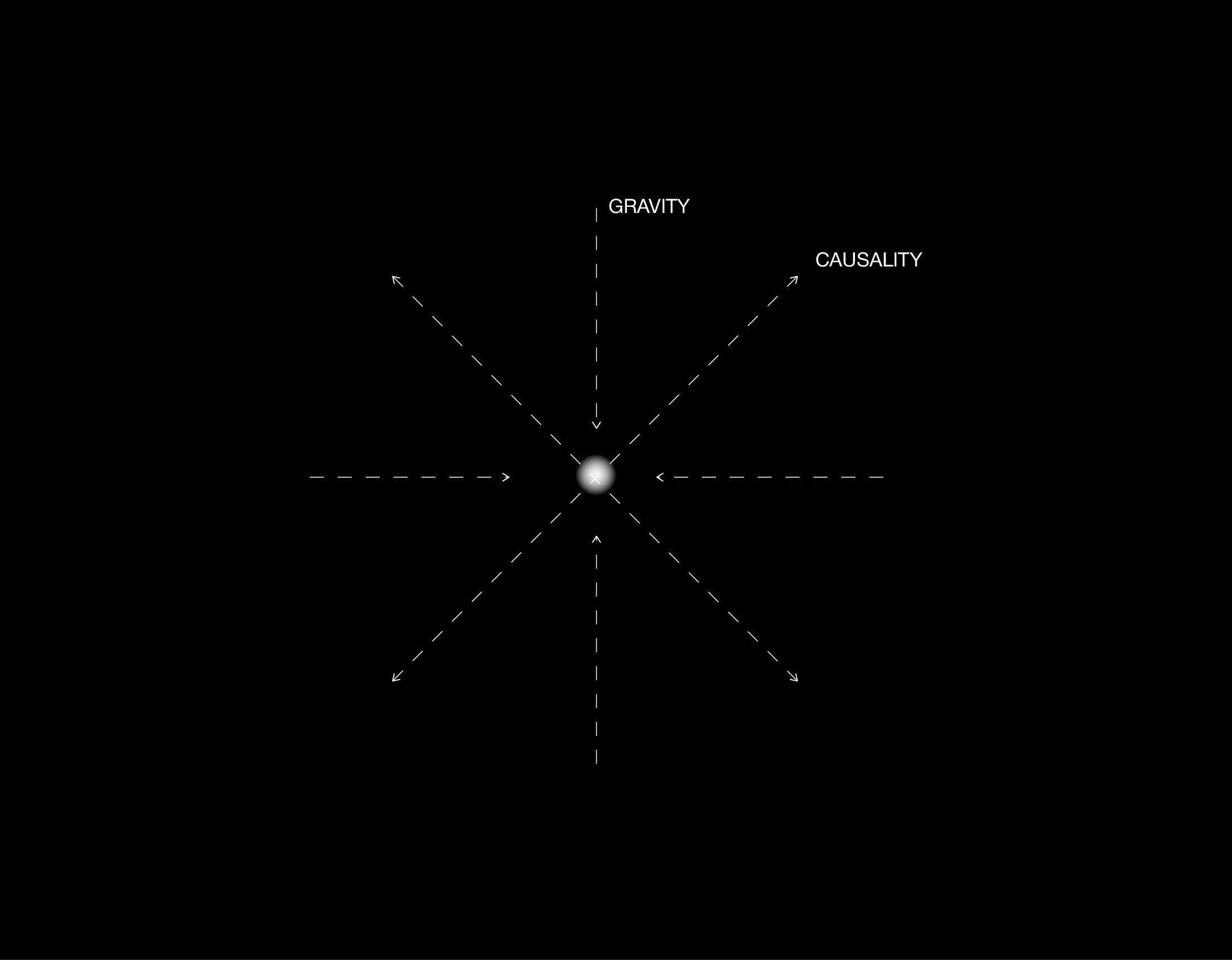
6 Cognitive Gravity, Time, and Causality
If causality emerges through gradients of cognitive gravity, then a deeper form of relativity arises, one that transcends the classical model of directional causation from A to B. In Cognitive Relativity, every event is relational, not linear; meaning does not follow from sequence but from resonance within a shared manifold. The intrinsic cognitive nature of physical reality, combined with the superposition of observer and observed, collapses the notion of causality into a perceptual effect, a secondary trace of decoherence within evolving cognitive structures.
Causality, in this framework, is not a fundamental force but a local illusion of order, an echo of the manifold stabilizing briefly around the observer’s recursive position. What we call cause and effect is a perceptual residue of deeper gravitational fluctuations within the field of consciousness.
Cognitive relativity reframes this entirely: the “now” becomes the only certainty, and both space and time collapse into observer-dependent constructs. The classical model of spacetime must be updated to reflect the continuum of experience and perception folding upon itself. Space and time are no longer absolute containers but components of the same cognitive structure, the reflection of consciousness within its own dimensional architecture.
7 Conclusion
- [ References]
- Achim, A.M., Lepage, M. (2005). Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex involvement in memory post-retrieval monitoring revealed in both item and associative recognition tests. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.10.036
- Armstrong, T., Detweiler-Bedell, B. (2008). Beauty as an Emotion: The Exhilarating Prospect of Mastering a Challenging World. Review of General Psychology, Vol. 12, pp 305-329, https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012558
- Archer, K., Catenacci Volpi, N., Bröker, F., & Polani, D. (2022). A space of goals: the cognitive geometry of informationally bounded agents. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2111.03699
- Arnheim, R. (2009). The Power of the Center: A Study of Composition in the Visual Arts (25th Anniversary ed.). University of California Press.
- Aston-Jones, G., & Waterhouse, B. (2016). Locus coeruleus: From global projection system to adaptive regulation of behavior. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.03.001
- Aston-Jones, G., & Cohen, J. D. (2005). An integrative theory of locus coeruleus-norepinephrine function: Adaptive gain and optimal performance. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.28.061604.135709
- Ayzenberg, V., Kamps, F.S., Dilks, D.S, Lourenco, S.F. (2022) Skeletal representations of shape in the human visual cortex. Neuropsychologia, Vol. 164. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2021.108092
- Balietti S. (2020). The human quest for discovering mathematical beauty in the arts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2018652117
- Bar, M. (2007). The proactive brain: using analogies and associations to generate predictions. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2007.05.005
- Baier, S., & Standaert, S. (2020). Gravity models and empirical trade. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Economics and Finance. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190625979.013.327
- Bejczy, A., Kim, W., Venema, S. (1990). The phantom robot: predictive displays for teleoperation with time delay. Proceedings., IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.1990.126037
- Bergson, H. (1896). Matter and Memory. Zone Books, New York.
- Bernardi S., Benna, M.K., Rigotti M., Munuera J., Fusi, S., Salzman D. (2020). The Geometry of Abstraction in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.031
- Bertamini, M., Helmy, M., Bates, D. (2013). The visual system prioritizes locations near corners of surfaces (not just locations near a corner). Attention, perception & psychophysics. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-013-0514-1
- Bihan, D. Le, Turner, R., Zeffiro, T., Cuénod, C., Jezzard, P., Bonnerot, V. (1993). Activation of Human Primary Visual Cortex During Visual Recall: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.90.24.11802
- Biederman, I., & Vessel, E. A. (2006). Perceptual pleasure and the brain: A novel theory explains why the brain craves information and seeks it through the senses. American Scientist, 94(3), 247–253. https://www.jstor.org/stable/27858773
- Boccia et al. (2016). Where does brain neural activation in aesthetic responses to visual art occur? Meta-analytic evidence from neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.09.009
- Borelli, C., Berneburg, M. (2009). Beauty lies in the eye of the beholder’? Aspects of beauty and attractiveness. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1610-0387.2009.07318_supp.x
- Borello, L., Ferraro, M., Penengo, P., Rossotti, M.L. (2004). A Model of Visual Perception. Biological Cybernetics. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336733
- Borst, de A.W., Sack, A.T., Jansma, B.M., Esposito, F., De Martino, F. (2012). Integration of “what” and “where” in frontal cortex during visual imagery of scenes. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.005
- Brashier, N. M., Marsh, E. (2019). Judging Truth. Annual Review of Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010419-050807
- Cameron, R.P. (2008). Truthmakers and ontological commitment: or how to deal with complex objects and mathematical ontology without getting into trouble. Philosophical Studies, Vol. 140, pp 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11098-008-9223-3
- Carter, J. (2019). Visual Thinking in Mathematics. Philosophy. https://doi.org/10.1093/obo/9780195396577-0229
- Chen, W., Kato, T., Zhu, X.H., Ogawa, S., Tank, D., Uğurbil, K. (1998). Human Primary Visual Cortex and Lateral Geniculate Nucleus Activation During Visual Imagery. Neuroreport. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199811160-00019
- Chung, S.Y, Abbott, L.F. (2021). Neural population geometry: An approach for understanding biological and artificial neural networks. DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2021.10.010
- Clark, A. (2015). Radical predictive processing. https://doi.org/10.1111/SJP.12120
- Clos, M., Kaller, C.P., & Eickhoff, S.B. (2019). The Influence of Dopamine on Cognitive Flexibility Is Mediated by the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13: 1163. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01286
- Correia, F. (2010). Grounding and truth-functions. Logique et Analyse, 53(211), 251–279. https://www.jstor.org/stable/44084957
- Costa da, N. C. A. (1989). Logic and Pragmatic Truth. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0049-237X(08)70049-1
- Cotler, J., & Strominger, A. (2025). Gravitational memory in quantum gravity. Physical Review D. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.111.066001
- Crain, S. M., Shen, K. F. (1990). Opioids can evoke direct receptor-mediated excitatory effects on sensory neurons. Trends in pharmacological sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-6147(90)90322-Y
- Dang, L., O’Neil, J., Jagust, W. (2012). Dopamine Supports Coupling of Attention-Related Networks. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0909-12.2012
- De Brigard, F. (2012). The Role of Attention in Conscious Recollection. Frontiers in Psychology, 3:29. doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00029
- De keersmaecker, J. et al. (2019). Investigating the Robustness of the Illusory Truth Effect Across Individual Differences in Cognitive Ability, Need for Cognitive Closure, and Cognitive Style. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167219853844
- Di Dio, C. et al. (2007). The Golden Beauty: Brain Response to Classical and Renaissance Sculptures. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001201
- Di Dio, C. et al. (2011). Specificity of Esthetic Experience for Artworks: An fMRI Study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2011.00139
- Di Dio, C. et al. (2016). Human, Nature, Dynamism: The Effects of Content and Movement Perception on Brain Activations during the Aesthetic Judgment of Representational Paintings. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00705
- Dimitrov, D., & Kroumpouzos, G. (2023). Beauty perception: A historical and contemporary review. Clinics in Dermatology, 41(1), 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2023.02.006
- Eagly, A., Ashmore, R., Makhijani, M. G., Longo, L. (1991). What is beautiful is good, but…: A meta-analytic review of research on the physical attractiveness stereotype. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.110.1.109
- Eichenbaum, H. (2014). Time cells in the hippocampus: a new dimension for mapping memories. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15(11), 732–744. doi: 10.1038/nrn3827
- Einevoll, G. T. (2006). Mathematical Modelling of Neural Activity. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-5030-5_8
- Enquist, M., Arak, A. (1994). Symmetry, beauty and evolution. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/372169A0
- Esposito, U. R., Kornetsky, C. (1978). Opioids and Rewarding Brain Stimulation. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/0149-7634(78)90052-0
- Fazio, L.K., Sherry, C.L. (2019). The Effect of Repetition on Truth Judgments Across Development. Psychology Science. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/36mqc
- Frégnac, Y., Rudolph, M., Davison, A.P, Destexhe, A. (2007). Complexity in Neuronal Networks. Complex Systems and Interdisciplinary Science, Biological Networks, pp. 291-340 https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812772367_0009
- Ganis, G., Thompson, W.L., Kosslyn, S.M. (2004). Brain Areas Underlying Visual Mental Imagery and Visual Perception: An fMRI Study. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COGBRAINRES.2004.02.012
- Garcia, C.G., Lesne, A., Hütt, M., Hilgetag, C. (2012). Building Blocks of Self-Sustained Activity in a Simple Deterministic Model of Excitable Neural Networks. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2012.00050
- Geniusas, S. (2021). Conscious and Unconscious Phantasy and the Phenomenology of Dreams. Research in Phenomenology. https://doi.org/10.1163/15691640-12341470
- Gruber, H., Clark, W. (1956). Perception of Slanted Surfaces. https://doi.org/10.2466/pms.1956.6.3.97
- Heusser, C., Fitzpatrick, C.P, Manning, J.R. (2018). Geometric models reveal behavioural and neural signatures of transforming experiences into memories. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01051-6
- Head, K and T Mayer (2014). Gravity Equations: Workhorse, Toolkit, and Cookbook. Chapter 3 in G Gopinath, E Helpman, and K S Rogoff (eds), Handbook of International Economics, Vol. 4, Elsevier.
- Isik, A. I., Vessel, E.A. (2021). From Visual Perception to Aesthetic Appeal: Brain Responses to Aesthetically Appealing Natural Landscape Movies. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.676032
- Jimenez, J.P. (2017). Unconscious fantasy (or phantasy) as clinical concept. The International journal of psycho-analysis. https://doi.org/10.1111/1745-8315.12513
- Johnson, S.G.B., Steinerberger, S. (2019). Intuitions about Mathematical Beauty: A Case Study in the Aesthetic Experience of Ideas. Cognition 189: 242-259; DOI: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.04.008
- Jones, J. (1992). Endorphins: The Basis of Pleasure? Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.55.4.247
- Keil, M.S., Cristóbal G., Neumann, H. (2006). Gradient Representation and Perception in the Early Visual System—A Novel Account of Mach Band Formation. Vision Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2006.01.038
- Keil, S. (2007). Gradient Representations and the Perception of Luminosity. Vision Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2007.09.018
- King, D., Auschaitrakul, S. (2020). Symbolic Sequence Effects on Consumers’ Judgments of Truth for Brand Claims. DOI: 10.1002/jcpy.1132
- Knauer, A., & Maloney, W. J. M. A. (1913). A Preliminary Note On The Psychic Action Of Mescalin, With Special Reference To The Mechanism Of Visual Hallucinations. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 40, 425–437 DOI: 10.1097/00005053-191307000-00001
- Knauff, M., Kassubek, J., Mulack, T., Greenlee, M. (2000). Cortical Activation Evoked by Visual Mental Imagery as Measured by fMRI. NeuroReport. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200012180-00011
- Kobayashi, K., & Hsu, M. (2019). Common neural code for reward and information value. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(26), 13061–13066. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820145116
- Kosslyn, M., Thompson, W.L., Klm, I.J., Alpert, N.M. (1995). Topographical Representations of Mental Images in Primary Visual Cortex. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/378496A0
- Kosslyn, S., Alpert, N., Thompson, W., Maljkovic, V., Weise, S., Chabris, C., Hamilton, S. E., Rauch, S., Buonanno, F. (1993). Visual Mental Imagery Activates Topographically Organized Visual Cortex: PET Investigations. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.1993.5.3.263
- Krupic, J., Bauza, M., Burton, S., Barry, C., O’Keefe, J. (2015). Grid cell symmetry is shaped by environmental geometry. Nature. DOI:10.1038/nature14153.
- Lakoff, G. (1973). Hedges: A study in meaning criteria and the logic of fuzzy concepts. J. Philos. Log. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262952
- Lakoff, G. (2003). Metaphors We Live By. University of Chicago Press. ISBN: 0226468011
- Lappin, S., Norman, J.F., Phillips, F.. (2011). Fechner, Information, and Shape Perception. Attention, Perception & Psychophysics. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-011-0197-4
- Le Merrer, J., Becker, J., Befort, K., Kieffer, B. (2009). Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiological Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00005.2009
- Leder, H., Belke, B., Oeberst, A., & Augustin, D. (2004). A model of aesthetic appreciation and aesthetic judgments. British Journal of Psychology, 95(4), 489–508. doi.org/10.1348/0007126042369811
- Lefton, K. B., Wu, Y., Dai, Y., Okuda, T., Zhang, Y., Yen, A., Rurak, G. M., Walsh, S., Manno, R., Papouin, T., et al. (2025). Norepinephrine signals through astrocytes to modulate synapses. Science, 388(6748), 776–783. doi/10.1126/science.adq5480
- Lehky, R., Sejnowski, T.J. (1988). Network Model of Shape-from-Shading: Neural Function Arises from Both Receptive and Projective Fields. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/333452A0
- Lima-de-Faria, A. (2014). Molecular Origins of Brain and Body Geometry: Plato’s Concept of Reality is Reversed. Springer, 2014th edition.
- Lindell, A., Lindell, K.L. (2014). Beauty captures the attention of the beholder. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, Volume 26, 2014 – Issue 7, pp 768-780. https://doi.org/10.1080/20445911.2014.963111
- Lohmar, D. (2010). The Function of Weak Phantasy in Perception and Thinking. Handbook of Phenomenology and Cognitive Science, pp 159–177 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2646-0_9
- Luecking, S. (2019). Visual Teaching of Geometry and the Origins of 20th Century Abstract Art. Journal of Humanistic Mathematics. https://doi.org/10.5642/JHUMMATH.201902.03
- MacDonald, C.J., Tonegawa, S. (2021) Crucial role for CA2 inputs in the sequential organization of CA1 time cells supporting memory. Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences, Vol. 118. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2020698118
- Maddy, P. (1988). Believing the axioms. I. Journal of Symbolic Logic (JSL). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022481200028425
- Mather, M., et al. (2016). The Locus Coeruleus: Essential for Maintaining Cognitive Function and Behavior. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4761411/
- Mather, M. (2019). The locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system role in cognition and how it changes with aging. http://gero.usc.edu/labs/matherlab/files/2019/01/2018_9_MatherInPress.pdf
- Mizokami, Y., et al. (2014). Difference in brain activations during appreciating paintings and photographic analogs. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00478
- Mudrik, L., Deouell, L. (2022). Neuroscientific Evidence for Processing Without Awareness. Annual Review of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-110920-033151
- Nakamura, N.H., Sauvage, M.M. (2016). Encoding and reactivation patterns predictive of successful memory performance are topographically organized along the longitudinal axis of the hippocampus. Hippocampus, Vol. 26 (1), pp 67-75. DOI: 10.1002/hipo.22491
- Naqvi, S., et al. (2020). Shared heritability of face and brain shape distinct from cognitive traits. bioRxiv 2020.08.29.269258; DOI: 10.1101/2020.08.29.269258
- Niall, K. (2002). Visual imagery and geometric enthymeme: The example of Euclid I.1. Behavioral and Brain Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0140525x02420043
- Noel, J. (1997). Interpreting Aristotle’s Phantasia and Claiming its Role Within Phronesis. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:170694052
- Noel, J. (1999). Phronesis and Phantasia: Teaching with Wisdom and Imagination. Journal of Philosophy of Education, Vol. 33 (2), pp 277–286. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9752.00136
- O’Craven, K., Kanwisher, N. (2000). Mental Imagery of Faces and Places Activates Corresponding Stimulus-Specific Brain Regions. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1162/08989290051137549
- O’Gorman, N. (2005). Aristotle’s Phantasia in the Rhetoric: Lexis, Appearance, and the Epideictic Function of Discourse. Philosophy & Rhetoric. https://doi.org/10.1353/PAR.2005.0009
- Owen, L.L.W., Chang, T., Manning, J. (2021). High-level cognition during story listening is reflected in high-order dynamic correlations in neural activity patterns. Nat Commun., Vol. 12(1). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25876-x
- Parr, T., Pezzulo, G., & Friston, K. (2022). Active Inference: The Free Energy Principle in Mind, Brain, and Behavior. MIT Press. https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/12441.001.0001
- Palmer, S., Schloss, K.B., Sammartino, J. (2013). Visual aesthetics and human preference. Annual Review of Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100504
- Perrett, D.I, et al. (1999). Symmetry and human facial attractiveness. Evolution and Human Behavior, Vol. 20 (5), pp 295-307. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1090-5138(99)00014-8
- Pejlare, J. (2007). On axioms and images in the history of Mathematics. Uppsala Dissertations in. Mathematics 53. 16 pp
- Pizer, M., Romeny, B. (1991). Fundamental properties of medical image perception. J Digit Imaging., DOI: 10.1007/BF03173870
- Priest, G. (2014). One: Being an Investigation into the Unity of Reality and of Its Parts, Including the Singular Object Which Is Nothingness. Oxford University Press. ISBN: 9780199688258
- Puig, M. V., Antzoulatos, E. G., Miller, E. K. (2014). Prefrontal dopamine in associative learning and memory. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.09.026
- Putnam, H. (1975). What is mathematical truth. Historia Mathematica, Vol. 2 (4), pp 529-533. https://doi.org/10.1016/0315-0860(75)90116-0
- Reber, R., Schwarz, N., & Winkielman, P. (2004). Processing Fluency and Aesthetic Pleasure: Is Beauty in the Perceiver’s Processing Experience? Personality and Social Psychology Review, 8(4), 364–382. doi: 10.1207/s15327957pspr0804_3.
- Reimann, M. W., Nolte, M., Scolamiero, M., Turner, K., Perin, R., Chindemi, G., Dłotko, P., Levi, R., Hess, K., & Markram, H. (2017). Cliques of neurons bound into cavities provide a missing link between structure and function. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 11, 48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2017.00048
- Rhodes, G., Proffitt, F., Grady, J.M., Sumich, A. (1998). Facial symmetry and the perception of beauty. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, Vol. 5, pp 659–669 https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03208842
- Rhodes, G., Zebrowitz, L A., Clark, A., Kalick S.M., Hightower, A., McKay, R. (2001). Do facial averageness and symmetry signal health? Evolution and human behavior. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1090-5138(00)00060-X
- Rivera, F. (2011). Visual Roots of Mathematical Cognitive Activity. Toward a Visually-Oriented School Mathematics Curriculum, pp 59–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0014-7_3
- Rock, I., & Gutman, D. (1981). The effect of inattention on form perception. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 7(2), 275–285.
- Sara, S. J. (2009). The locus coeruleus and noradrenergic modulation of cognition.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2573
- Sales A., Friston K., Jones M., Pickering A., Moran R (2019). Locus Coeruleus tracking of prediction errors optimises cognitive flexibility. https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pcbi.1006267
- Schacter, D. L., Addis, D. R. (2020). Memory and imagination: Perspectives on constructive episodic simulation. In A. Abraham (Ed.), The Cambridge handbook of the imagination, pp. 111–131. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108580298.008
- Scheib, J. E., Gangestad, S., Thornhill, R. (1999). Facial attractiveness, symmetry and cues of good genes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1999.0866
- Schwarz, N., Newman, E.J., Leach, W.R. (2016). Making the Truth Stick & the Myths Fade: Lessons from Cognitive Psychology. Behavioral Science & Policy, Vol. 2(1), pp 85-95 https://doi.org/10.1177/237946151600200110
- Segal, J. (1985). Phantasy in Everyday Life: A Psychoanalytical Approach to Understanding Ourselves. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429478253
- Segal, H. (1994). Phantasy and Reality. The International Journal of Psycho-analysis. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429484469-7
- Serrano, S., Smith, N.A. (2019). Is Attention Interpretable? Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P19-1282
- Sharpee, O.T, Rowekamp, R. (2017). Cross-orientation suppression in visual area V2. Nat Commun, Vol. 8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15739
- Sievers, B., Lee, C., Haslett, W., & Wheatley, T. (2019). A multi-sensory code for emotional arousal. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 286(1906), 20190513. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2019.0513
- Sinclair, N. (2011). Aesthetic Considerations in Mathematics. Journal of Humanistic Mathematics, 1(1), 2–32. DOI: 10.5642/jhummath.201101.03
- Skov, M., Nadal, M. (2020). The nature of beauty: behavior, cognition, and neurobiology. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, Vol. 1488, pp 44-55. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.14524
- Smith, J.H., et al (2021). How neurons exploit fractal geometry to optimize their network connectivity. Scientific Reports, Vol. 11, Article number: 2332. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81421-2
- Stokes, D. (2018). Cognitive Penetrability of Perception. Philosophy Compass 8 (7):646-663 (2013)
- Stewart, I. (2007). Why Beauty Is Truth: A History of Symmetry. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.45-0833
- Sohn, H., Narain, D, Nicolas, M., Jazayeri, M. (2019). Bayesian computation through Cortical Latent Dynamics. Neuron, Vol. 103, pp 934-947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.06.012
- Staudigl, T., Leszczynski, M., Jacobs, J., Schroeder, C. E., Jensen, O., & Doeller, C. F. (2018). Hexadirectional modulation of high-frequency electrophysiological activity in the human anterior medial temporal lobe maps visual space. Current Biology, 28(21), 3325–3329.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.09.031
Stepniewski, M., Breit, M.,Hoffer, M., - Queisser, G. (2019). NeuroBox: Computational Mathematics in Multiscale Neuroscience. Comput. Vis. Sci., Vol. 20, pp 111–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00791-019-00314-0
- Sun, J., Perona, P. (1996). Early Computation of Shape and Reflectance in the Visual System. Nature, Vol. 369, pp 165-168. https://doi.org/10.1038/379165A0
- Symington, N. (1985). Phantasy Effects That Which It Represents. The International Journal of Psycho-analysis, pp 349-357 https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:10631294
- Tamargo, R.J., Pindrik, J.A. (2019). Mammalian Skull Dimensions and the Golden Ratio, Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, Vol. 30(6), pp 1750-1755. DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005610
- Thompson, K.G. & Schall, J.D. (2000). Antecedents and correlates of visual detection and awareness in macaque prefrontal cortex.
- Vision Research, 40(10-12), 1523–1538
Tozzi, A. (2019). The Multidimensional Brain. Physics of Life Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plrev.2018.12.004 - Treisman, A.M., & Gelade, G. (1980). A feature-integration theory of attention. Cognitive Psychology, 12(1), 97–136.
- Truică, I. (2013). Arta compoziției. Ars Docendi. ISBN-10 : 973461889X
- Vartanian, O., & Goel, V. (2004). Neuroanatomical correlates of aesthetic preference for paintings. NeuroReport, 15(5), 893–897. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200404090-00032.
- Vessel, E.A., Starr, G., Rubin, N., Pascual-Leone, Á., Israel, B. (2012). The brain on art: intense aesthetic experience activates the default mode network. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00066
- Vessel, E.A., Isik A.I., Belfi A.M. (2019). The default-mode network represents aesthetic appeal that generalizes across visual domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., Vol. 116, pp 19155-19164, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1902650116.
- Warner, M. (2006). Phantasmagoria: Spirit Visions, Metaphors, and Media into the Twenty-first Century. New York: Oxford University Press. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:190743530
- White, A.M. (1993). Essays in Humanistic Mathematics. Mathematical Association of America. ISBN 0883850893, 9780883850893
- Whiteley, W. (2005). Teaching to see like a mathematician. Studies in Multidisciplinarity, Vol. 2, pp 279-292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1571-0831(04)80048-0
- Zhang, H., Rich, P.D., Lee, A.K., Sharpee, T.O. (2022). Hippocampal spatial representations exhibit a hyperbolic geometry that expands with experience. Nature Neuroscience, Vol. 26, pp131–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-022-01212-4
© 2025, Tib Roibu